Food Nucleic Acids Function
Beans and legumes promote healthy structure of your cells and muscles.
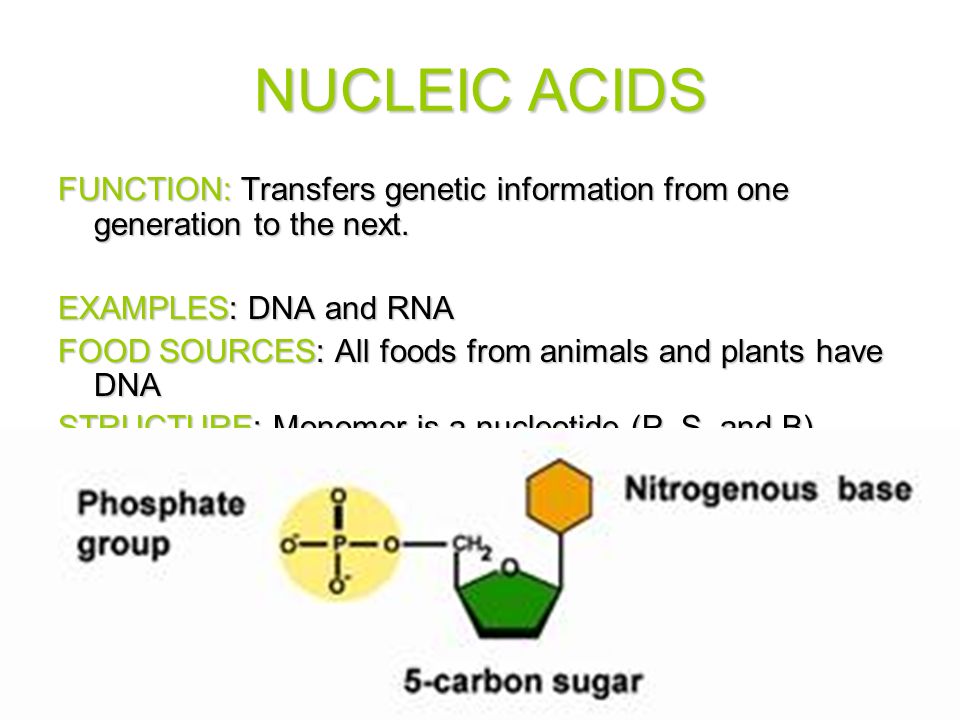
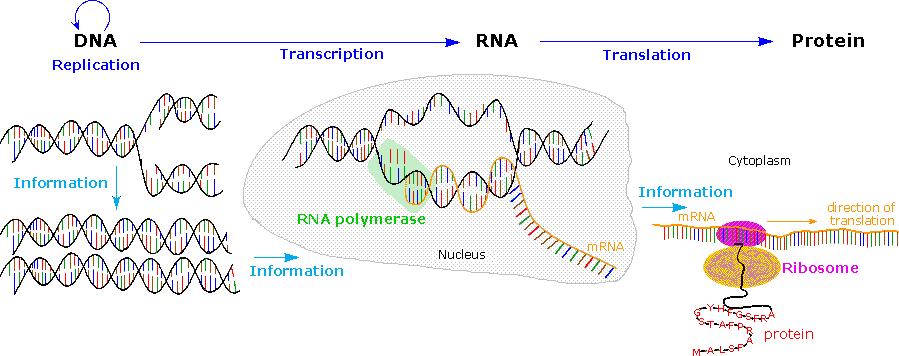
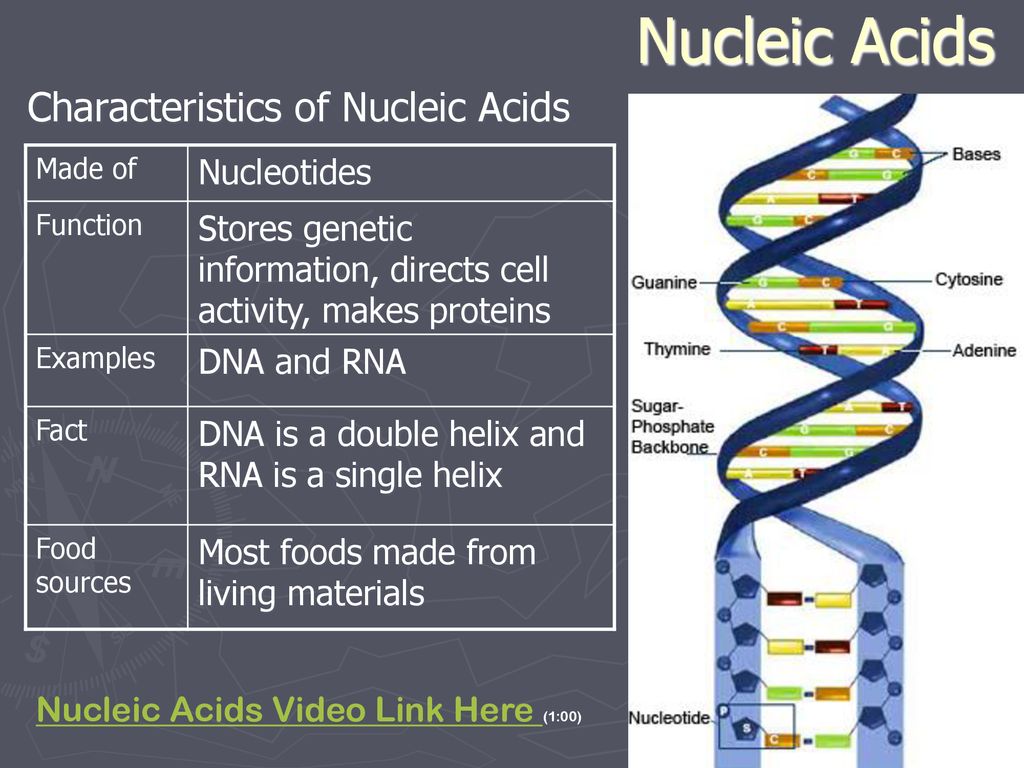
Food nucleic acids function. The nucleic acids dna and rna may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell. According to the gordon. The functions performed by these are as follows. Rna is also essential for protein synthesis.
In addition they contain a high level of proteins and dietary fiber. Updated january 25 2020. Foods that contain nucleic acids seafood. Nucleic acids are molecules that allow organisms to transfer genetic information from one generation to the next.
Nuts are excellent sources of proteins and unsaturated fats which are good for heart function. If you have children your genetic information will be recombined and united with your partners genetic. The carbon and nitrogen derived from these become the building block for nucleotides nucleic acids proteins cells and tissues. Nucleic acids store and transmit genetic information that you inherited from your parents.
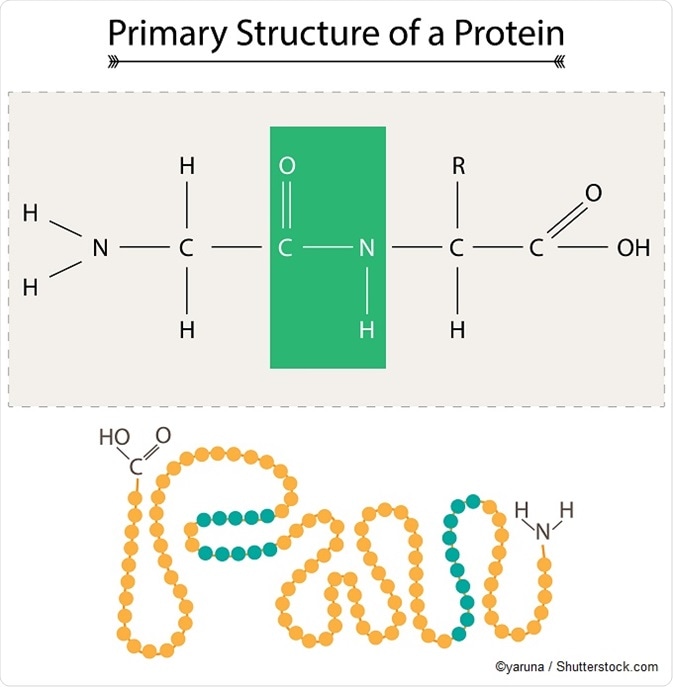
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and protein breakdown provides amino acids that are used for cellular function. Legumes and beans are rich in nucleic acid. A number of different seafood options contain nucleic acids particularly fish. The primary function of nucleic acids which in nature include dna and rna is to store and transfer genetic information.
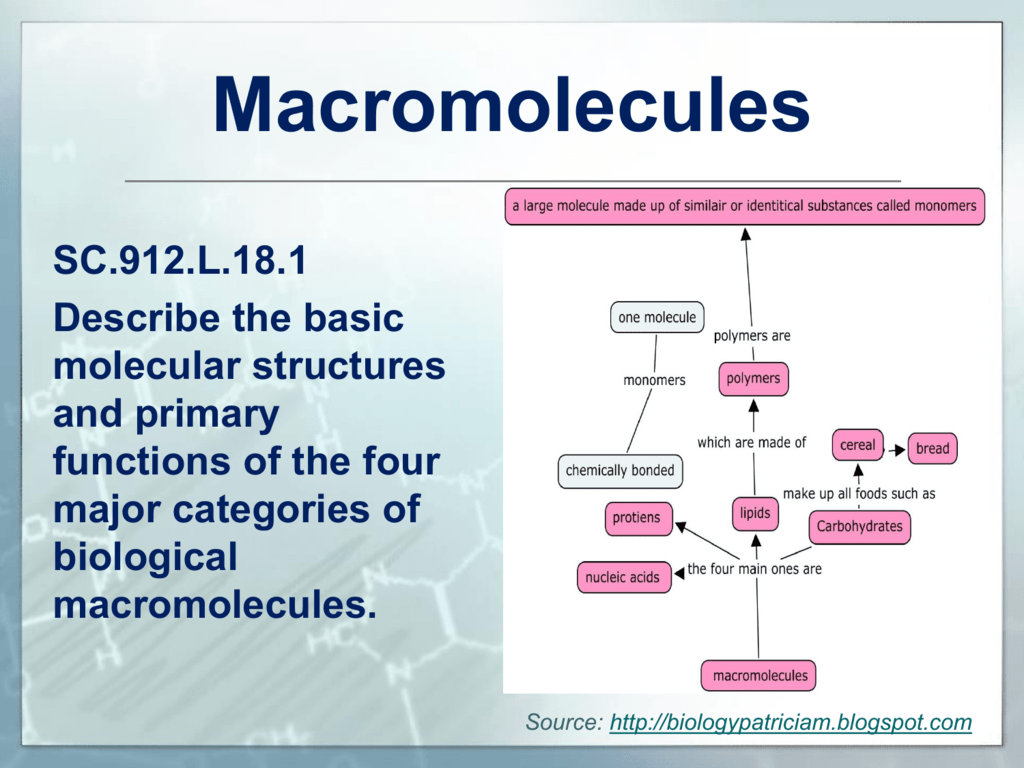
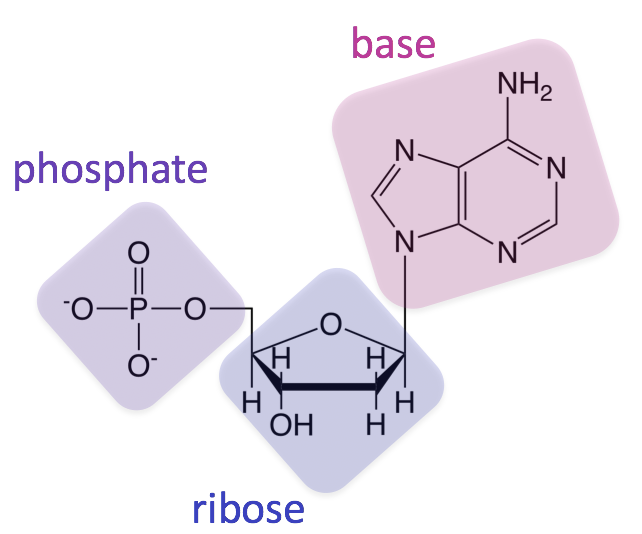
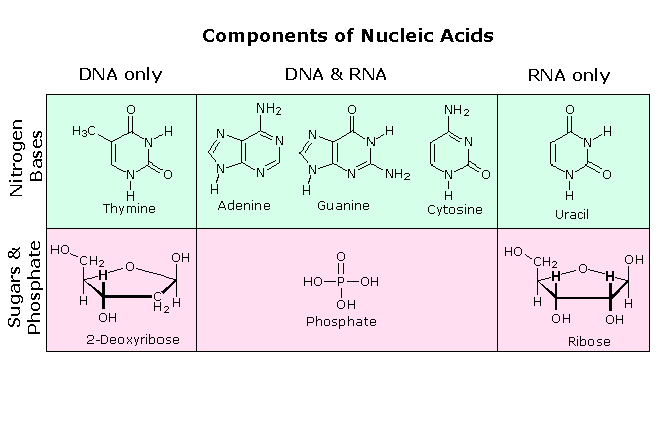
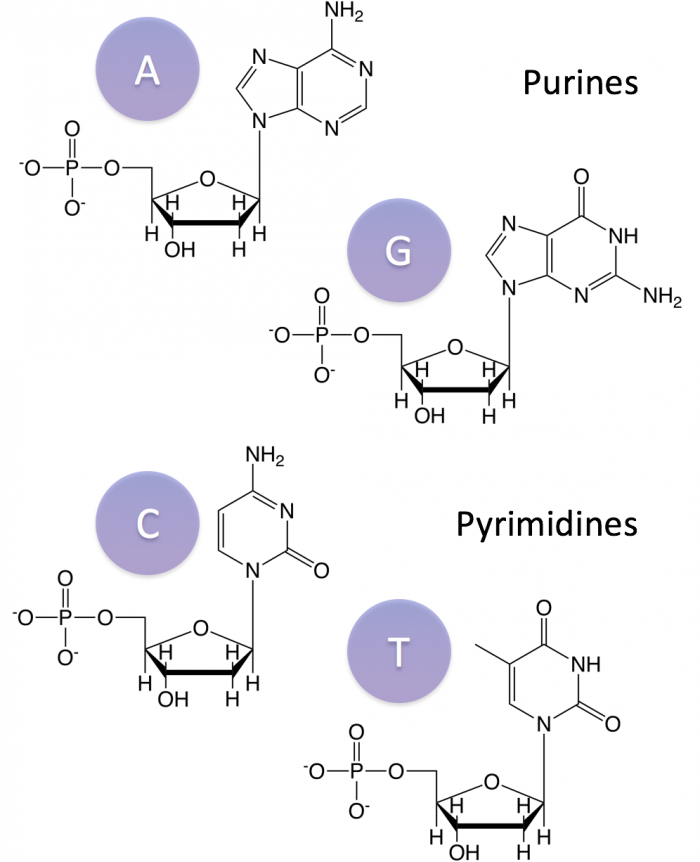
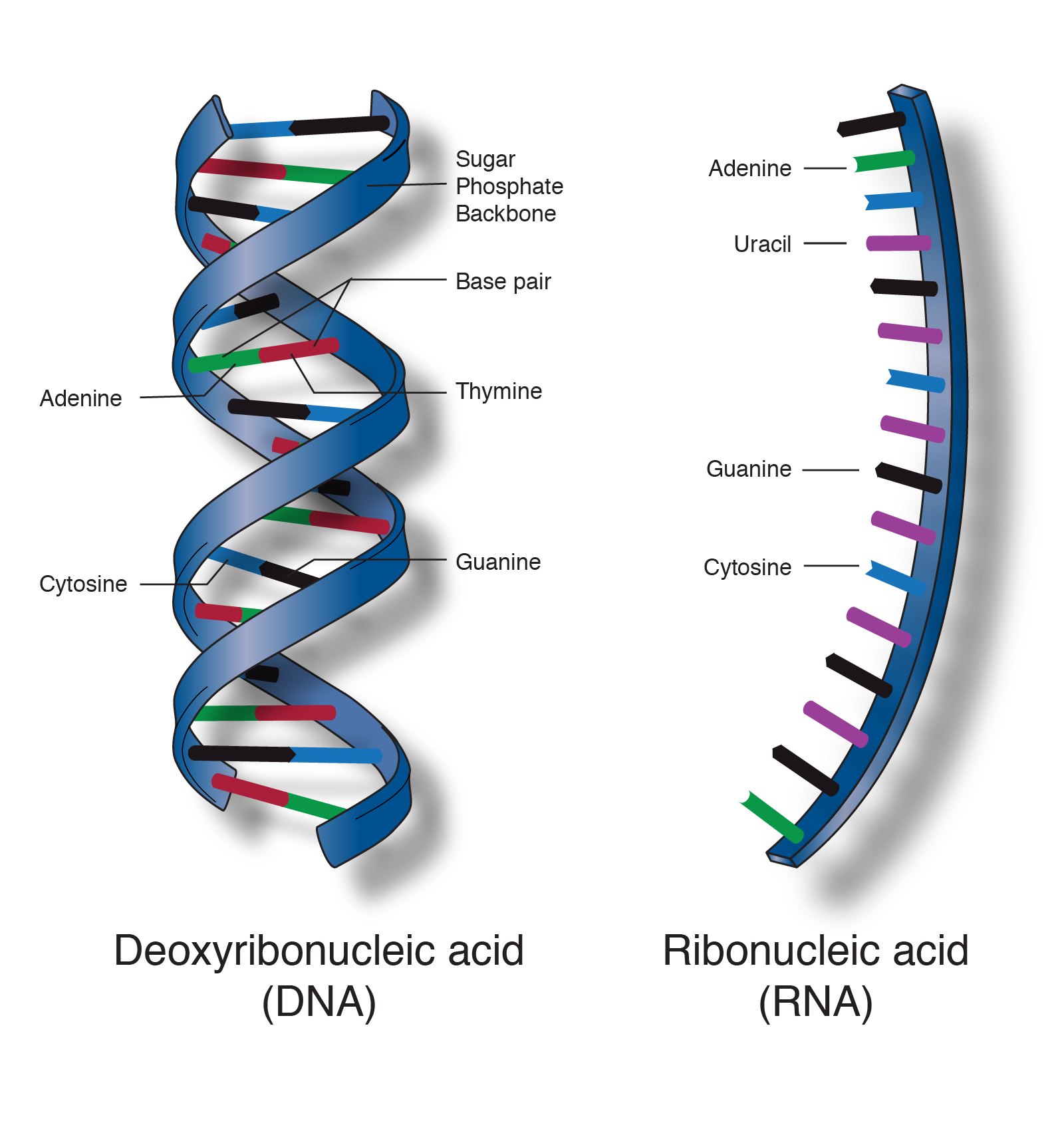
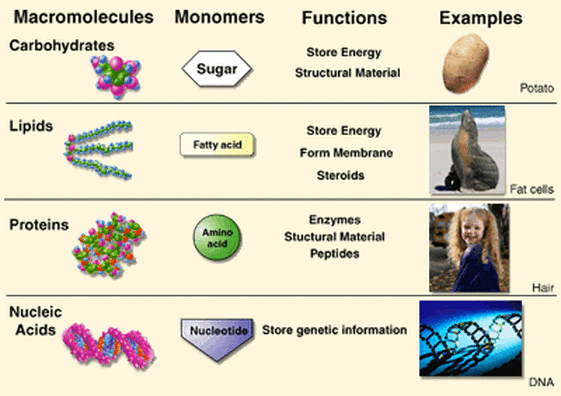
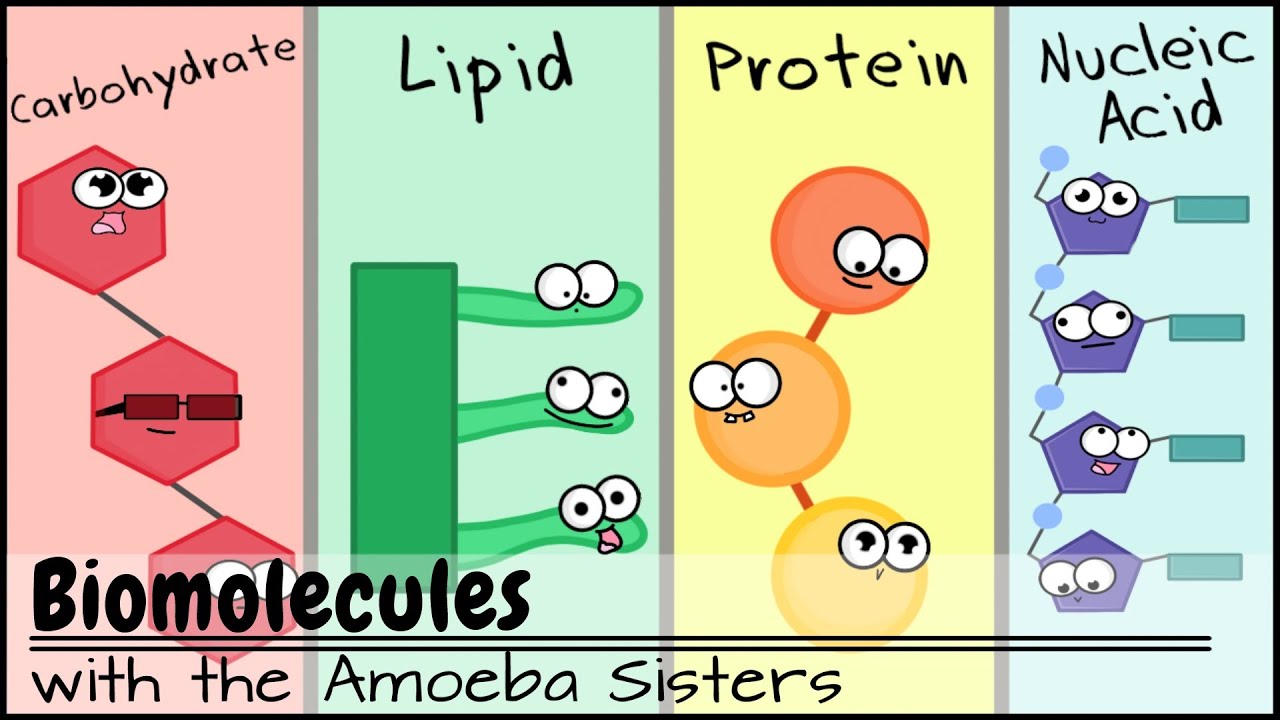
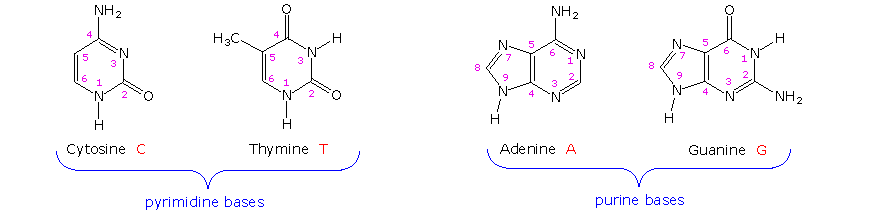
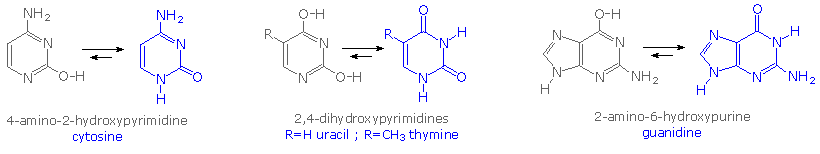
Nucleic acids are the main information carrying molecules of the cell and by directing the process of protein synthesis they determine the inherited characteristics of every living thing. Nucleic acids consist of nucleotides which in turn are composed of a sugar a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. Vegetables are a. Making nucleic acid foods part of your diet can be beneficial.
Nucleic acids mainly dna and rna play an essential role in the bodies of living organisms. Examples include clovers peas and lentils. Nucleic acids are a key component in cell regeneration and the transfer of hereditary information. These macromolecules store the genetic information that determines traits and makes protein synthesis possible.
Protein catabolism provides a source of organic nitrogen. Nucleic acids help synthesise proteins in the body.















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/RNA_vs_DNA-5b633a1fc9e77c002ca252a1.jpg)
















/nucleotides-5c253d8cc9e77c0001d9b089.jpg)













/DNAstructure-58c233583df78c353c23dbe6.jpg)











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DNA_nitrogenous_bases-5b63374b46e0fb00250bcaa1.jpg)




